250 Mg Per 5 Ml
To reduce the evolution of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral interruption, cephalexin tablets, and other antibacterial drugs, cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral interruption, and cephalexin tablets should be used only to treat or forbid infections that are proven or strongly suspected to exist caused by leaner.
DESCRIPTION
Cephalexin, USP is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic intended for oral assistants. It is seven-(D-α-amino-α-phenylacetamido)-iii-methyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid, monohydrate.
Cephalexin has the following structural formula:
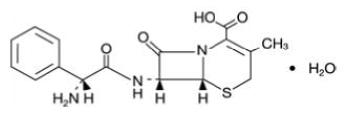
CxviH17NthreeO4Southward•H2O M.W. 365.41
The nucleus of cephalexin is related to that of other cephalosporin antibiotics. The compound is a zwitterion; i.eastward., the molecule contains both a basic and an acidic group. The isoelectric betoken of cephalexin in water is approximately 4.5 to 5.
The crystalline class of cephalexin which is bachelor is a monohydrate. It is a white crystalline solid having a bitter taste. Solubility in water is depression at room temperature; i or 2 mg/mL may be dissolved readily, just higher concentrations are obtained with increasing difficulty.
The cephalosporins differ from penicillins in the structure of the bicyclic ring organisation. Cephalexin has a D-phenylglycyl group every bit substituent at the vii-amino position and an unsubstituted methyl grouping at the iii-position.
Each sheathing contains cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 250 mg (720 μmol) or 500 mg (ane,439 μmol) of cephalexin.
Inactive Ingredients: CAPSULES: magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide, and sodium starch glycolate.
Capsule Shell and Print Constituents: black iron oxide, D&C Yellow #10 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue #1 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Bluish #2 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Red #40 Aluminum Lake, gelatin, pharmaceutical glaze modified in SD-45, silicon dioxide or carboxymethylcellulose sodium, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide and may contain propylene glycol. In improver, the 250 mg capsule shell contains yellow iron oxide.
After mixing, each 5 mL of cephalexin for oral suspension USP will comprise cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 125 mg (360 μmol) or 250 mg (720 μmol) of cephalexin.
Inactive Ingredients: Pause: FD&C Red #twoscore, cherry mixed fruit flavor (artificial flavors, benzyl booze, maltodextrin, and modified corn starch), silicon dioxide, sodium benzoate, saccharide (fruit granulated), and xanthan mucilage.
Each tablet contains cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 250 mg (720 μmol) or 500 mg (1,439 μmol) of cephalexin.
Inactive Ingredients: TABLETS: hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, sodium starch glycolate, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Man Pharmacology
Cephalexin is acid stable and may be given without regard to meals. It is rapidly absorbed later on oral administration. Following doses of 250 mg, 500 mg, and 1 g, average pinnacle serum levels of approximately 9, eighteen, and 32 mcg/mL, respectively were obtained at i hour. Measurable levels were present 6 hours after assistants. Cephalexin is excreted in the urine by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Studies showed that over 90% of the drug was excreted unchanged in the urine within 8 hours. During this menstruation, peak urine concentrations following the 250 mg, 500 mg, and ane g doses were approximately 1000, 2200, and 5000 mcg/mL, respectively.
Microbiology
In vitro tests demonstrate that the cephalosporins are bactericidal because of their inhibition of prison cell-wall synthesis. Cephalexin has been shown to be agile against virtually strains of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
Aerobes, Gram-positive:
Staphylococcus aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains)
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains)
Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobes, Gram-negative:
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis
Proteus mirabilis
Annotation—Methicillin-resistant staphylococci and most strains of enterococci (Enterococcus faecalis [formerly Streptococcus faecalis]) are resistant to cephalosporins, including cephalexin. Information technology is not active against most strains of Enterobacter spp., Morganella morganii, and Proteus vulgaris. Information technology has no activity against Pseudomonas spp. or Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae is usually cross-resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics.
Susceptibility Tests
Dilution techniques
Quantitative methods are used to make up one's mind antimicrobial minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC's). These MIC'due south provide estimates of the susceptibility of leaner to antimicrobial compounds. The MIC's should exist determined using a standardized process. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method1-3 (broth or agar) or equivalent with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of cephalothin powder. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
| MIC (mcg/mL) | Estimation |
| ≤ viii | Susceptible (S) |
| 16 | Intermediate (I) |
| ≥ 32 | Resistant (R) |
A written report of "Susceptible" indicates that the pathogen is probable to exist inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the claret reaches the concentrations usually achievable. A report of "Intermediate" indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically viable drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone which prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of "Resistant" indicates that the pathogen is not likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable; other therapy should be selected.
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory command microorganisms to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. Standard cephalothin powder should provide the following MIC values:
| Microorganism | MIC (mcg/mL) |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 4 to 16 |
| Southward. aureus ATCC 29213 | 0.12 to 0.5 |
Diffusion techniques
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. 1 such standardized procedure2,3 requires the utilize of standardized inoculum concentrations. This procedure uses newspaper disks impregnated with thirty mcg cephalothin to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to cephalexin.
Reports from the laboratory providing results of the standard unmarried-disk susceptibility test with a xxx mcg cephalothin disk should exist interpreted according to the following criteria:
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation |
| ≥ 18 | Susceptible (South) |
| 15 to 17 | Intermediate (I) |
| ≤ 14 | Resistant (R) |
Estimation should be as stated above for results using dilution techniques. Estimation involves correlation of the diameter obtained in the disk test with the MIC for cephalexin.
As with standard dilution techniques, diffusion methods require the use of laboratory control microorganisms that are used to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. For the diffusion technique, the 30 mcg cephalothin disk should provide the following zone diameters in these laboratory test quality control strains:
| Microorganism | Zone Diameter (mm) |
| Eastward. coli ATCC 25922 | 15 to 21 |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 29 to 37 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cephalexin is indicated for the treatment of the following infections when acquired by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms:
Respiratory tract infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes (Penicillin is the usual drug of option in the treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever. Cephalexin is mostly effective in the eradication of streptococci from the nasopharynx; all the same, substantial data establishing the efficacy of cephalexin in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available at nowadays.)
Otitis media due to Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Moraxella catarrhalis
Skin and pare structure infections caused past Staphylococcus aureus and/or Streptococcus pyogenes
Bone infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and/or Proteus mirabilis
Genitourinary tract infections, including acute prostatitis, caused by Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae
Notation—Civilisation and susceptibility tests should be initiated prior to and during therapy. Renal part studies should be performed when indicated.
To reduce the evolution of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral suspension, cephalexin tablets, and other antibacterial drugs, cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral suspension, and cephalexin tablets should be used only to treat or foreclose infections that are proven or strongly suspected to exist caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cephalexin is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
WARNINGS
BEFORE THERAPY WITH CEPHALEXIN IS INSTITUTED, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE TO DETERMINE WHETHER THE PATIENT HAS HAD PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO CEPHALEXIN, CEPHALOSPORINS, PENICILLINS, OR OTHER DRUGS. IF THIS Product IS TO Exist GIVEN TO PENICILLIN-SENSITIVE PATIENTS, Circumspection SHOULD Exist EXERCISED Considering Cross-HYPERSENSITIVITY AMONG BETA-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS HAS BEEN CLEARLY DOCUMENTED AND MAY OCCUR IN Upwardly TO x% OF PATIENTS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION TO CEPHALEXIN OCCURS, DISCONTINUE THE DRUG. SERIOUS Astute HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS MAY REQUIRE Handling WITH EPINEPHRINE AND OTHER EMERGENCY MEASURES, INCLUDING OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS, INTRAVENOUS ANTIHISTAMINES, CORTICOSTEROIDS, PRESSOR AMINES AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, Equally CLINICALLY INDICATED.
There is some clinical and laboratory evidence of partial cross-allergenicity of the penicillins and the cephalosporins. Patients have been reported to have had astringent reactions (including anaphylaxis) to both drugs.
Any patient who has demonstrated some form of allergy, specially to drugs, should receive antibiotics cautiously. No exception should be made with regard to cephalexin.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of well-nigh all antibacterial agents, including cephalexin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile crusade increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must exist considered in all patients who present with diarrhea post-obit antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months later the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted every bit clinically indicated.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Prescribing cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral suspension, or cephalexin tablets in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the evolution of drug-resistant bacteria.
Patients should be followed carefully and then that any side furnishings or unusual manifestations of drug idiosyncrasy may be detected. If an allergic reaction to cephalexin occurs, the drug should be discontinued and the patient treated with the usual agents (e.g., epinephrine or other pressor amines, antihistamines, or corticosteroids).
Prolonged use of cephalexin may result in the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Conscientious observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Positive direct Coombs' tests have been reported during handling with the cephalosporin antibiotics. In hematologic studies or in transfusion cantankerous-matching procedures when antiglobulin tests are performed on the minor side or in Coombs' testing of newborns whose mothers have received cephalosporin antibiotics earlier parturition, it should exist recognized that a positive Coombs' examination may be due to the drug.
Cephalexin should be administered with caution in the presence of markedly dumb renal function. Under such weather, careful clinical ascertainment and laboratory studies should exist made considering safe dosage may be lower than that ordinarily recommended.
Indicated surgical procedures should be performed in conjunction with antibiotic therapy.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of gastrointestinal disease, particularly colitis.
Cephalosporins may be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional land, too as patients receiving a protracted class of antimicrobial therapy, and patients previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at gamble and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral suspension, and cephalexin tablets should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They practise non treat viral infections (east.g., the common common cold). When cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral pause, or cephalexin tablets are prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should exist told that although it is mutual to feel better early in the class of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full class of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increment the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cephalexin capsules, cephalexin for oral suspension, cephalexin tablets, or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused past antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and encarmine stools (with or without breadbasket cramps and fever) even as late as ii or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician equally shortly every bit possible.
Drug Interactions
Metformin
In healthy subjects given unmarried 500 mg doses of cephalexin and metformin, plasma metformin mean Cmax and AUC increased by an boilerplate of 34% and 24%, respectively, and metformin mean renal clearance decreased by xiv%. No information is available about the interaction of cephalexin and metformin following multiple doses of either drug.
Although not observed in this study, adverse furnishings could potentially arise from coadministration of cephalexin and metformin by inhibition of tubular secretion via organic cationic transporter systems. Accordingly, careful patient monitoring and dose adjustment of metformin is recommended in patients concomitantly taking cephalexin and metformin.
Probenecid
As with other β-lactams, the renal excretion of cephalexin is inhibited by probenecid.
Drug/Laboratory Examination Interactions
Equally a result of administration of cephalexin, a false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine may occur. This has been observed with Benedict'southward and Fehling'due south solutions and also with Clinitest® tablets.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Lifetime studies in animals accept not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of cephalexin. Tests to determine the mutagenic potential of cephalexin have not been performed. In male and female rats, fertility and reproductive performance were not afflicted by cephalexin oral doses up to 1.5 times the highest recommended human dose based upon mg/m2.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy category B
Reproduction studies have been performed on mice and rats using oral doses of cephalexin monohydrate 0.6 and 1.5 times the maximum daily man dose (66 mg/kg/24-hour interval) based upon mg/m2, and have revealed no harm to the fetus. At that place are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because fauna reproduction studies are not always predictive of man response, this drug should exist used during pregnancy simply if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
The excretion of cephalexin in human milk increased up to four hours after a 500 mg dose; the drug reached a maximum level of 4 mcg/mL, then decreased gradually, and had disappeared viii hours afterward administration. Circumspection should be exercised when cephalexin is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of cephalexin in pediatric patients was established in clinical trials for the dosages described in the DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section. In these trials, pediatric patients may have received cephalexin capsules or cephalexin for oral suspension. Cephalexin capsules should only be used in children and adolescents capable of ingesting the capsule.
Geriatric Utilise
Of the 701 subjects in iii published clinical studies of cephalexin, 433 (62%) were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted past the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may exist greater in patients with impaired renal role. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, intendance should be taken in dose selection, and information technology may be useful to monitor renal function (see PRECAUTIONS, General).
Agin REACTIONS
Gastrointestinal
Onset of pseudomembranous colitis may occur during or subsequently antibacterial treatment (see WARNINGS). Nausea and vomiting take been reported rarely. The most frequent side effect has been diarrhea. It was very rarely severe enough to warrant cessation of therapy. Dyspepsia, gastritis, and abdominal hurting have likewise occurred. As with some penicillins and some other cephalosporins, transient hepatitis and cholestatic jaundice have been reported rarely.
Hypersensitivity
AlIergic reactions in the grade of rash, urticaria, angioedema, and, rarely, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis have been observed. These reactions usually subsided upon discontinuation of the drug. In some of these reactions, supportive therapy may be necessary. Anaphylaxis has also been reported.
Other reactions have included genital and anal pruritus, genital moniliasis, vaginitis and vaginal belch, dizziness, fatigue, headache, agitation, defoliation, hallucinations, arthralgia, arthritis, and joint disorder. Reversible interstitial nephritis has been reported rarely. Eosinophilia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, and slight elevations in AST and ALT take been reported.
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above that accept been observed in patients treated with cephalexin, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin form antibiotics:
Adverse Reactions
Fever, colitis, aplastic anemia, hemorrhage, renal dysfunction, and toxic nephropathy.
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients
with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE
and PRECAUTIONS, General). If seizures associated with drug therapy should occur, the
drug should exist discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
Altered Laboratory Tests
Prolonged prothrombin fourth dimension, increased BUN, increased creatinine, elevated alkaline
phosphatase, elevated bilirubin, elevated LDH, pancytopenia, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE EVENTS, contact FDA at ane-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov.
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of oral overdose may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea, and hematuria. If other symptoms are nowadays, information technology is probably secondary to an underlying disease land, an allergic reaction, or toxicity due to ingestion of a second medication.
Treatment
To obtain upwards-to-appointment information about the treatment of overdose, a good resources is your certified Regional Toxicant Control Center. Telephone numbers of certified poison command centers are listed in the Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR). In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug overdoses, interaction among drugs, and unusual drug kinetics in your patient.
Unless 5 to 10 times the normal dose of cephalexin has been ingested, gastrointestinal decontamination should not be necessary.
Protect the patient'south airway and support ventilation and perfusion. Meticulously monitor and maintain, within acceptable limits, the patient's vital signs, blood gases, serum electrolytes, etc. Assimilation of drugs from the alimentary canal may be decreased past giving activated charcoal, which, in many cases, is more effective than emesis or lavage; consider charcoal instead of or in add-on to gastric emptying. Repeated doses of charcoal over time may hasten emptying of some drugs that have been absorbed. Safeguard the patient's airway when employing gastric elimination or charcoal.
Forced diuresis, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or charcoal hemoperfusion accept not been established equally beneficial for an overdose of cephalexin; nonetheless, it would be extremely unlikely that one of these procedures would be indicated.
The oral median lethal dose of cephalexin in rats is > 5000 mg/kg.
DOSAGE AND Administration
Cephalexin is administered orally.
Adults
The developed dosage ranges from 1 to iv g daily in divided doses. The 333 mg and 750 mg strengths should be administered such that the daily dose is inside ane to 4 grams per mean solar day. The usual developed dose is 250 mg every half dozen hours. For the post-obit infections, a dosage of 500 mg may exist administered every 12 hours: streptococcal pharyngitis, skin and skin structure infections, and unproblematic cystitis in patients over fifteen years of age. Cystitis therapy should be continued for 7 to 14 days. For more severe infections or those acquired by less susceptible organisms, larger doses may be needed. If daily doses of cephalexin greater than 4 m are required, parenteral cephalosporins, in appropriate doses, should be considered.
Pediatric Patients
The usual recommended daily dosage for pediatric patients is 25 to 50 mg/kg in divided doses. For streptococcal pharyngitis in patients over 1 year of age and for pare and skin structure infections, the total daily dose may be divided and administered every 12 hours.
| Cephalexin Suspension | ||
| Weight | 125 mg/five mL | 250 mg/five mL |
| 10 kg (22 lb) | i/ii to 1 tsp q.i.d. | ane/4 to 1/2 tsp q.i.d. |
| xx kg (44 lb) | 1 to 2 tsp q.i.d. | 1/ii to 1 tsp q.i.d. |
| twoscore kg (88 lb) | 2 to iv tsp q.i.d. | 1 to 2 tsp q.i.d. |
| or | ||
| Weight | 125 mg/5 mL | 250 mg/5 mL |
| ten kg (22 lb) | 1 to ii tsp b.i.d. | one/2 to 1 tsp b.i.d |
| 20 kg (44 lb) | two to iv tsp b.i.d. | 1 to two tsp b.i.d. |
| 40 kg (88 lb) | four to eight tsp b.i.d. | two to 4 tsp b.i.d. |
In severe infections, the dosage may exist doubled.
In the therapy of otitis media, clinical studies have shown that a dosage of 75 to 100 mg/kg/24-hour interval in 4 divided doses is required.
In the handling of β-hemolytic streptococcal infections, a therapeutic dosage of cephalexin should be administered for at to the lowest degree ten days.
Directions for Mixing
125 mg per 5 mL (100 mL when mixed): Fix suspension at time of dispensing. Add to the bottle a total of 71 mL of water. For ease in training, tap bottle to loosen pulverisation, add the water in ii portions, shaking well later on each addition. The resulting suspension will contain cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 125 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
125 mg per five mL (200 mL when mixed): Prepare suspension at time of dispensing. Add together to the bottle a total of 140 mL of water. For ease in preparation, tap bottle to loosen pulverization, add the water in two portions, shaking well after each addition. The resulting interruption will contain cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 125 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
250 mg per five mL (100 mL when mixed): Prepare suspension at time of dispensing. Add to the canteen a full of 71 mL of water. For ease in training, tap bottle to loosen pulverization, add the h2o in 2 portions, shaking well after each improver. The resulting suspension will incorporate cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 250 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
250 mg per 5 mL (200 mL when mixed): Prepare suspension at time of dispensing. Add to the canteen a total of 140 mL of water. For ease in preparation, tap bottle to loosen powder, add the water in 2 portions, shaking well later on each addition. The resulting suspension will contain cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 250 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
* After mixing, store in refrigerator. May be kept for 14 days without significant loss of potency.
HOW SUPPLIED
Cephalexin for oral suspension* USP
(a cherry mixed fruit flavored formula)—
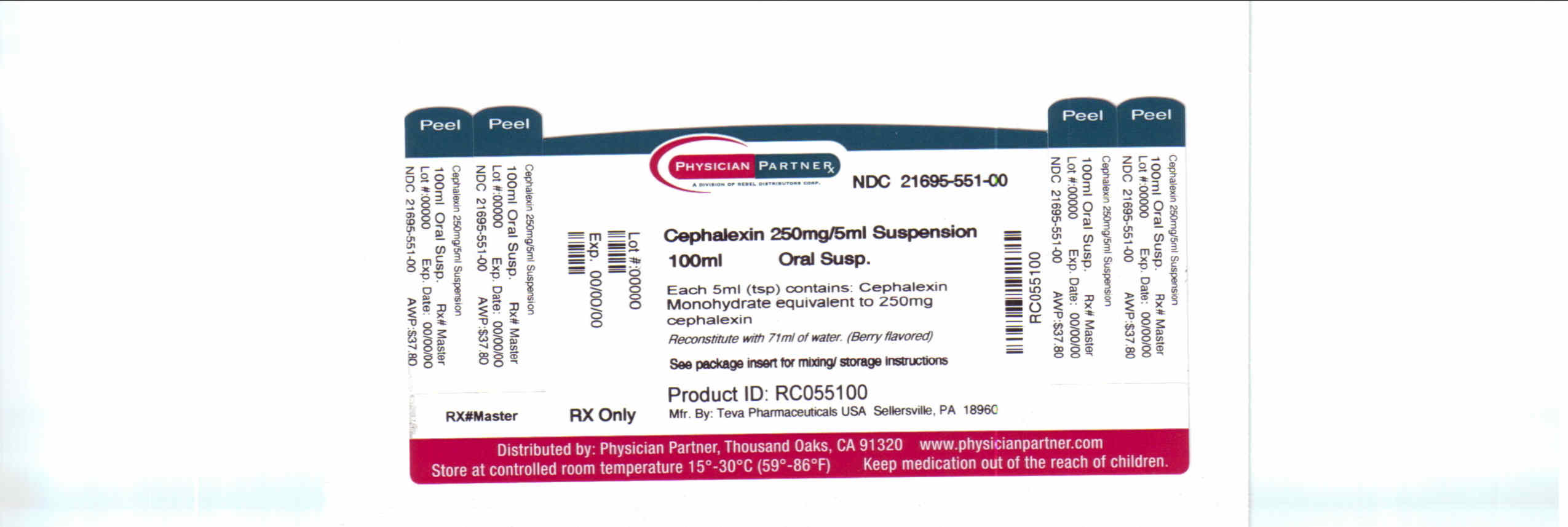
125 mg/5 mL: bottles of 200 mL NDC 21695-789-20.
250 mg/5 mL: bottles of 100 mL NDC 21695-551-00 and 200 mL NDC 21695-551-xx.
Directions for mixing are included on the characterization.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [Run into USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Shake well earlier using. Keep tightly airtight.
* Subsequently mixing, store in refrigerator. May be kept for fourteen days without significant loss of potency.
REFERENCES
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically — 4th Edition. Canonical Standard NCCLS Document M7-A4, Vol. 17, No. 2, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 1997.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Operation Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests — Sixth Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M2-A6, Vol. 17, No. 1, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, Jan, 1997.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Functioning Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing — 8th Advisory Supplement. Canonical Standard NCCLS Document M100-S8, Vol. xviii, No. i, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 1998.
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS U.s.
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. Northward 1/2010
Repackaged by:
Rebel DISTRIBUTORS CORP
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Main DISPLAY PANEL
250 Mg Per 5 Ml,
Source: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=4e334e50-19c4-449b-b77f-549a461c7f84
Posted by: kelleywoming.blogspot.com


0 Response to "250 Mg Per 5 Ml"
Post a Comment